Navigating Duodenal Switch Surgery: What You Should Be Aware Of
Duodenal Switch Surgery – For those living with severe obesity, major weight loss can dramatically improve health. One option to achieve significant weight reduction is duodenal switch surgery. This complex procedure combines restrictive stomach reduction with intestinal alteration to promote rapid pound shedding and improvement of obesity-linked diseases.
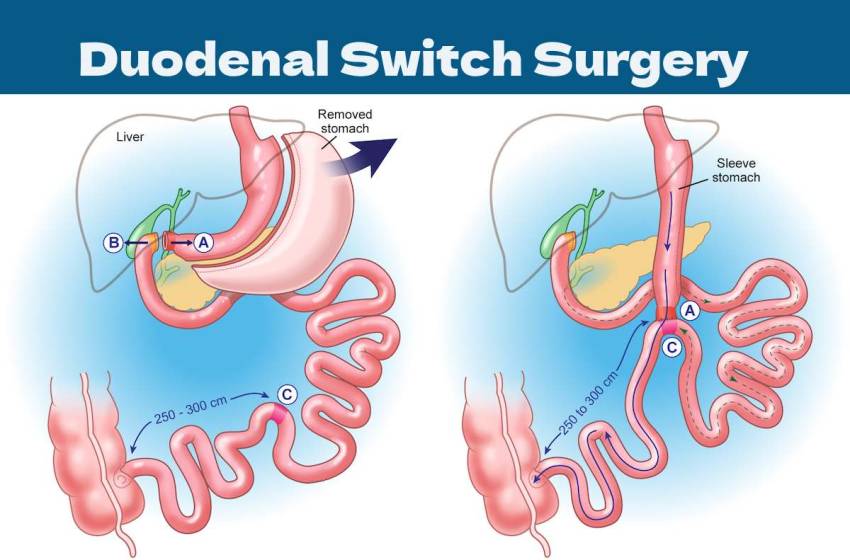
During duodenal switch surgery, also called biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS), the bulk of the stomach is removed to form a small pouch, limiting food capacity. Additionally, the digestive system is rerouted to reduce calorie uptake from food. By incorporating restriction and an altered metabolic process, patients can finally attain lasting weight loss after years of failed dieting. Alongside weight reduction, recovery of associated diseases like diabetes and hypertension may occur.
Table of Contents
Duodenal Switch Surgery: How It Works
The duodenal switch uses two main surgical changes to spur weight loss. First, the surgeon removes 70-80% of the patient’s stomach pouch, leaving only a tiny sack the size of a golf ball behind. This minimized stomach strictly limits food intake, enabling initial fat burning. Second, the first part of the small intestine is rerouted so fewer calories are absorbed, even on the miniature stomach. By substantially cutting both intake capacity and nutrient absorption ability, rapid weight drops are stimulated through this two-pronged surgical approach.
Candidates for Duodenal Switch
This intensive surgery is generally recommended for those with severe obesity (BMI over 50) suffering from poorly controlled weight-related conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. For such patients unable to slim down sufficiently through diet and lifestyle changes alone, duodenal switch surgery may finally offer a solution. By instantly limiting food intake and absorption, substantial weight loss becomes possible for those struggling to lose pounds through non-surgical means. Additionally, significant improvement of associated diseases often occurs after surgery due to the direct links between excess weight and these health issues.
What to Expect: The Procedure and Recovery
Lasting several hours, duodenal switch surgery is performed under general anesthesia. Patients usually remain in the hospital for monitoring for 2-4 days post-surgery before being discharged home. Adjusting food choices and quantities is crucial during recovery to allow proper healing without overtaxing the altered digestive system. Dietary changes needing to be maintained long-term are introduced gradually.
The Benefits and Considerations
Along with rapid and significant weight loss, recovery of obesity-related diseases commonly occurs after duodenal switch surgery. However, such a dramatic change in digestion poses risks. Nutritional deficiencies may arise over time, necessitating supplements and testing. As with any major surgery, short-term surgical risks also warrant consideration.
Conclusion
For those with a high BMI and obesity-linked illness not improving through other efforts, duodenal switch surgery may offer new hope. This intensive procedure promotes radical weight loss and enhanced well-being via a reconfigured digestive system. However, permanent lifestyle shifts around eating and supplementation are mandatory after surgery to stay healthy.
By coupling a minimally sized stomach pouch with disrupted nutrient absorption, the duodenal switch furnishes significant weight reduction in excess of that from standard dieting. However, an enduring commitment is essential to adapting to and adhering to the lifelong alterations this surgery necessitates for ideal results. Well-informed patients ready to make such changes may find this operation a pathway out of obesity when less extreme methods have not been successful. Consulting specialists can illuminate what life post-op fully entails.


