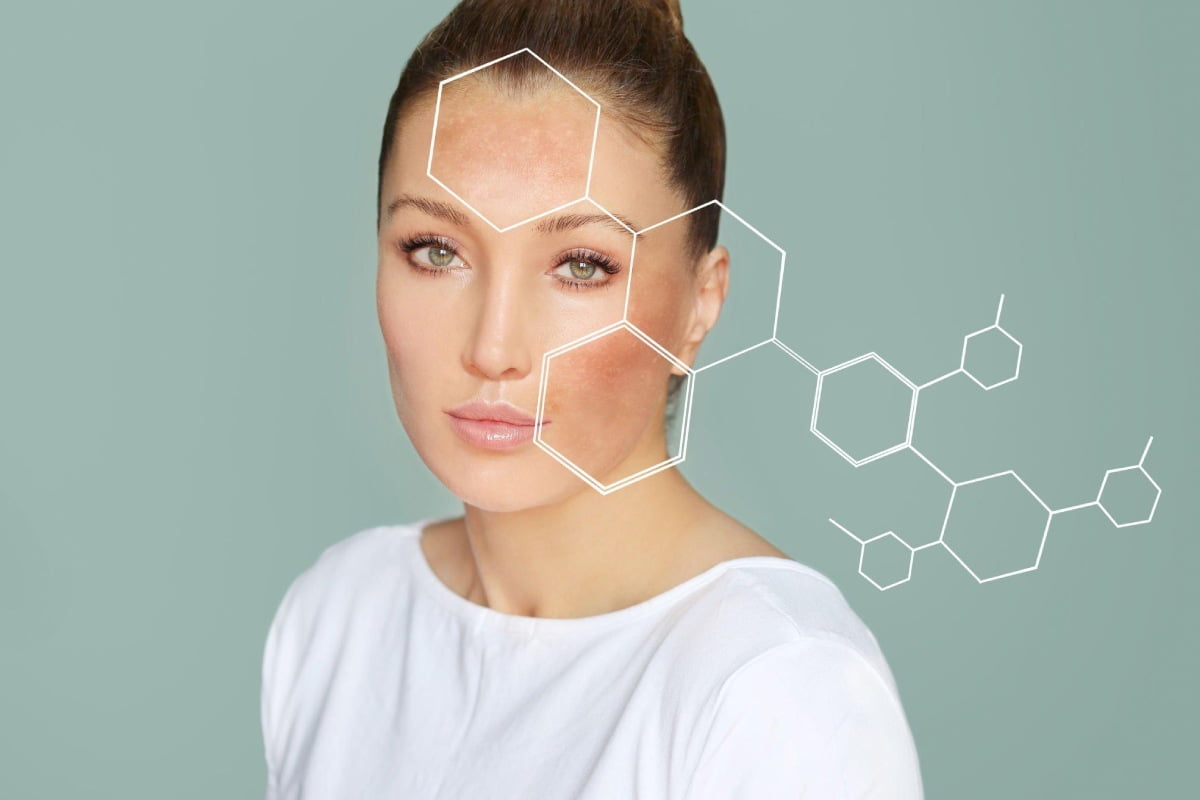

Signs You Have Sun Damage
The sunshine may feel great (not to mention it’s necessary for your vitamin D levels) but it’s also not that kind to our skin: Sun damage, also known as photoaging, can take a permanent toll on your appearance. If your anti-aging face masks haven’t been working like usual, then you might have sustained sun damage without even knowing it. Read on to discover what causes sun damage, signs of photoaging, and what you can do to prevent and treat sun damage.
What Causes Sun Damage?
While sun rays may look the same to the naked eye, they involve three different types of ultraviolet (UV) radiation that can damage your skin:
- UVA light: This type of solar radiation affects all layers of the skin, from the epidermis down into the dermis, and can damage the collagen and elastic in your skin. UVA rays mostly contribute to long-term skin damage, such as wrinkles and hyperpigmentation.
- UVB light: This type of radiation only affects the epidermis, but it can damage DNA more than UVA can. UVB rays are a big contributor to signs of photoaging, as well as raising your risk of skin cancer; these are also the type of sun rays that cause sunburns.
- UVC light: This type of radiation is largely absorbed by the atmosphere and ozone layer, so we mostly don’t have to worry about it. Thus, you will see UVA and UVB protection referenced on sunscreen, but rarely UVC.
When shopping for anti-aging sunscreen, look for one that offers “broad spectrum protection,” which means that it is effective against both UVA and UVB rays. Some sunscreen filters only protect against one or the other, so it’s important that your skin is safe from both types of solar radiation.

Signs You Have Sun Damage
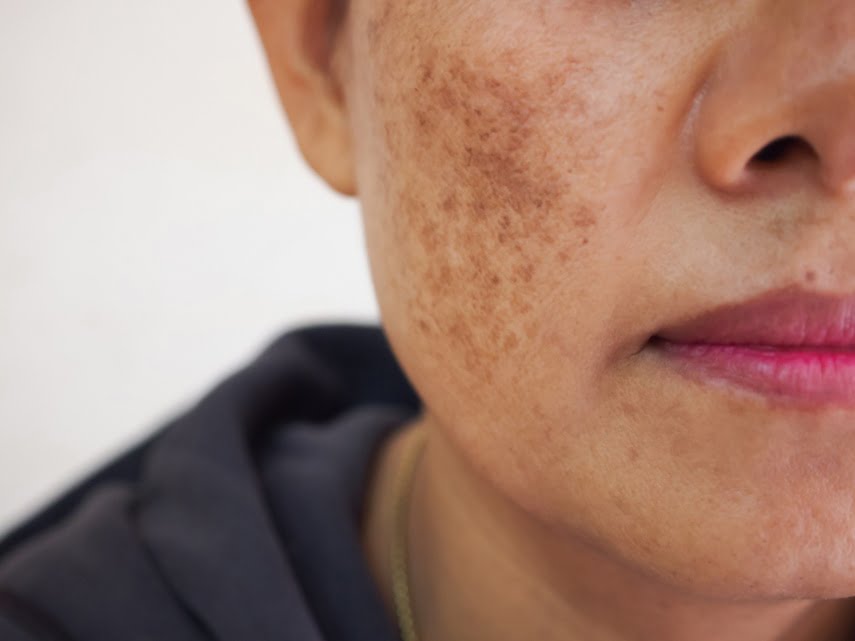
A sunburn is the most obvious sign that your skin has been damaged by the sun, but there are many other signs to look for as well. For one, you might experience hyperpigmentation changes such as liver spots, age spots, and freckles. You might also experience melasma, which are larger patches of pigmented skin, often found along the cheeks.
Even if you don’t sunburn or experience hyperpigmentation, you might still find your skin looking red and blotchy. Some people also experience a more severe form of this, rosacea, which can be temporary or more permanent. Broken capillaries (spider veins) may also appear, especially around the nose and on the chest.
Wrinkles and fine lines are also signs of cumulative sun damage. In fact, some of those signs of aging that you have been noticing recently might be indications that you’re not getting enough sun protection. Sun damage also contributes to loss of skin tone and decreased elasticity within the skin, and you may notice that your skin feels thinner as well.
In some cases, people develop rough, scaly patches called actinic keratosis in response to sun damage. Sometimes these patches can appear on the lips as well as the face; these lip lesions are officially known as actinic cheilitis. Chronic sun exposure increases your risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers, which can manifest as atypical moles and other growths. If you have been noticing skin growths suddenly appearing, or changes in existing moles, see a dermatologist right away for a biopsy and treatment.

How to Prevent and Treat Sun Damage
One of the best things that you can do to both prevent and treat photoaging is to wear sunscreen every single day on all exposed parts of your skin. Windows don’t do a very good job blocking UV rays, so it’s important to weather sunscreen even if you are sitting inside all day. The sunscreen should be at least SPF 30, and ideally higher if you are already suffering from sun damage. Choose a water resistant sunscreen if you sweat a lot or are planning to get in and out of the water. Re-apply every two hours to ensure that you stay covered.
Don’t rely on sunscreen alone, however: UPF clothing, hats, and sunglasses will all help protect your skin from the sun. Seek shade whenever possible, especially when the sun is the strongest between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Whatever you do, don’t deliberately lie out in the sun and tan or get in a tanning bed — sunless tanning products are much safer and don’t contain harmful UV rays.
If you are already seeing the signs of sun damage, you can try different topical treatments to see if they work. Retinols and retinoids encourage faster skin cell turnover and can help to treat minor signs of photoaging. Exfoliating skin care products will help to address texture issues and smooth out skin; never use them on a sunburn, as they can make it worse. Vitamin C and other antioxidants will help to brighten the skin and prevent further damage from free radicals. Lightening agents such as hydroquinone will help to fade hyperpigmentation over time.
Topical skincare products can be effective, but they take time to work and they may not be strong enough to address serious signs of sun damage. Meanwhile, dermatologist’s offices offer a variety of professional treatments that can address sun damage, including laser resurfacing, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, cryotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and more. If you’d like to explore these treatment options, book a consultation with a dermatologist to discuss which one might be the best fit for you.
What do you do to stay on top of sun protection? Have you gotten a professional dermatology treatment for photoaging? Have any topical products worked to face your sun damage? We want to hear from you, so let us know in the comments below!


