Everything You Need To Know About Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
When we dive into the molecular world that orchestrates the symphony of life, few players are as critical as Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, or NAD+. This coenzyme is at the heart of numerous metabolic processes, acting as a vital player in the biochemical dance that powers our cells and, by extension, us. It’s involved in processes ranging from energy production to DNA repair, making it a focal point of scientific research and health discussions. Understanding NAD+ is essential for those keen on optimizing health and longevity. Keep reading to explore the ways this molecule impacts our bodies.
Table of Contents
Understanding Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
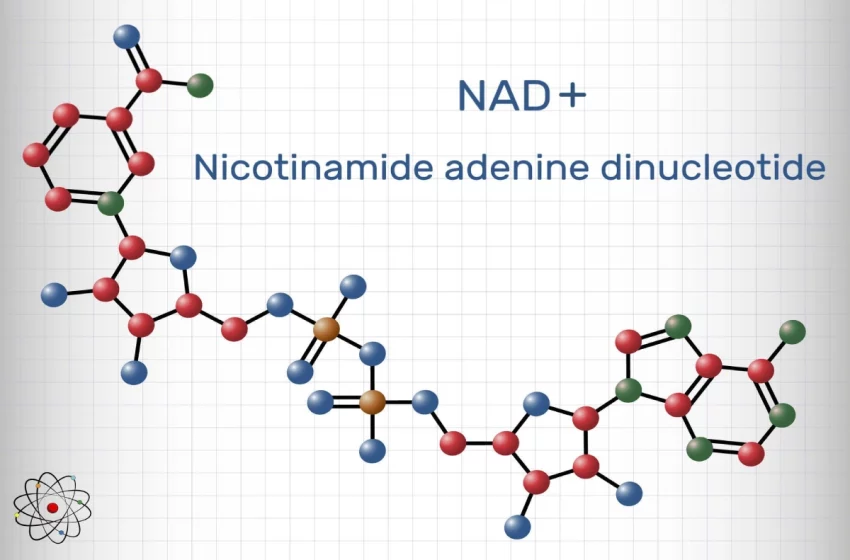
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, or NAD+, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. It’s a crucial part of the energy conversion process, acting as a shuttle for electrons during the metabolic reactions that release energy from nutrients. Without NAD+, cells couldn’t access the life-sustaining energy stored in the foods we consume.
Structurally, NAD+ consists of two nucleotides joined together by their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base, and the other nicotinamide. In its chemical intricacies, NAD exists in two forms: the oxidized NAD+ and the reduced NADH, each playing unique roles in cellular metabolism.
The importance of this molecule stretches far beyond energy production. It also plays a part in maintaining the health of our DNA, regulating stress responses, and controlling the circadian rhythm. It’s a testament to the interconnectedness of our body’s functions that one molecule can be so multifaceted.
To comprehend the magnitude of NAD+’s role, researchers delve into its molecular mechanics and interactions. For a more comprehensive understanding of this powerful coenzyme, you can learn more about NAD at nad.com.
The Role of NAD+ in Cellular Metabolism and Energy Production

NAD+ sits at the core of metabolic reactions, particularly in the mitochondria, which are our cells’ proverbial power plants. Here, NAD+ picks up electrons from the breakdown of glucose and fatty acids, enabling the production of ATP — the universal energy currency of the cell.
This coenzyme also has a starring role in the electron transport chain, a series of reactions that are critical to ATP synthesis. Without sufficient levels of NAD+, this chain could not function effectively, leading to reduced energy production and compromised cell function.
Moreover, NAD+ impacts the activity of enzymes, notably the sirtuins that regulate metabolic processes and PARPs that manage DNA repair. By doing so, NAD+ influences aspects of cellular health that extend far beyond mere energy output.
Health Benefits of NAD+
Recent research has put a spotlight on the diverse health benefits tied to NAD+. With its role in repairing damaged DNA, it can mitigate the effects of oxidative stress and slow down cellular aging. These benefits make NAD+ a molecule of interest for those seeking to prolong the health and vitality of their cells.
Additionally, the link between NAD+ levels and age-related conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease suggests that maintaining robust NAD+ levels might be integral in protecting neurological health. High NAD+ levels have been associated with enhanced neuroplasticity and cognitive function.
The influence of NAD+ extends to metabolic disorders as well, with studies implying that it can improve insulin sensitivity and support better blood sugar management. This is promising for preventing or managing conditions like diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
The Impact of Age and Lifestyle on NAD+ Levels in the Body

As we grow older, the levels of NAD+ in our body tend to diminish, leading to a reduced capacity for cellular repair and energy production. This decline is thought to be a factor in the aging process and contributes to the onset of age-related health issues.
Lifestyle choices can profoundly impact NAD+ levels, with factors such as overeating, excessive alcohol consumption, and limited physical activity being detrimental. Conversely, calorie restriction, moderate exercise, and reduced exposure to sunlight have been shown to support NAD+ levels.
Stress, both physical and environmental, also plays a role. Chronic stress can deplete NAD+ reserves, while acute stress can trigger temporary increases in NAD+ as part of the body’s response mechanism. Thus, maintaining a balanced lifestyle is vital for preserving NAD+ at healthy levels.
Overall, the significance of NAD+ within the body’s metabolic and regulatory systems is undeniably profound. By acknowledging and responding to this molecular maestro through informed lifestyle choices and interventions, we may tap into one of the pillars of health and longevity. Supporting NAD+ levels can have lasting impacts on our well-being, revealing the exquisite complexity and adaptability of the human body.


