
The Science of Growing Old and How You Can Slow the Aging Process
Everyone knows that aging comes with its own set of problems. With body issues like changing blood pressure, cognitive decline, and poorer immune system function, seniors are generally weaker and aren’t able to fulfill actions they would have used to do. Yet despite this general trend, there are still people who are supercentenarians and have lived beyond 110 years of age.
How are they able to live so long?
Table of Contents
How the aging process works
Healthy longevity always seemed to be due to a good lifestyle of diet, exercise, and social interactions, combined with minimized smoking and overeating. But with the advent of scientific research, more reasons behind aging have been discovered- with several studies pointing towards the erosion of telomeres.
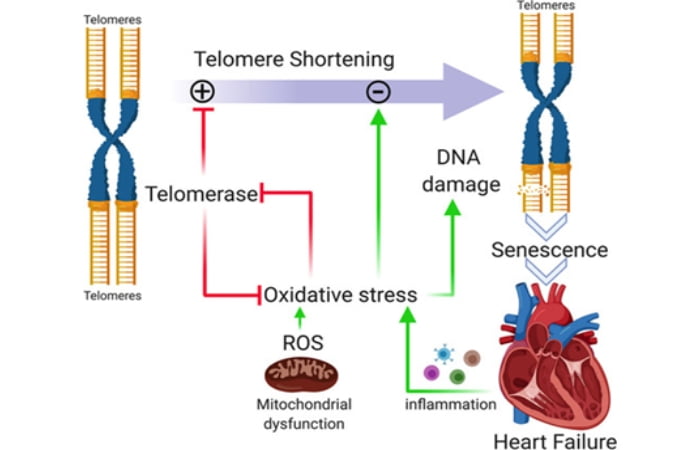
Within our cells, DNA is split into chromosomes that contain telomeres at their ends. These are meant to protect the DNA, much like the plastic tips at the end of our shoelaces.
Every time the cell divides, the telomeres erode bit by bit until the actual DNA is threatened. Unfortunately, this process may be sped up due to environmental factors like radiation and pollution. When the actual DNA is eroded, our cells decline in function and eventually manifest into age-related diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease, to name a few.
In the case of supercentenarians, they’ve been lucky not to face issues related to genetics. Growing old is inevitable, but several advancements in medical research have paved the way for novel therapeutics to make the aging process more bearable.
While certain studies have worked towards rejuvenating specific cells essential to the body, there are experimental studies working towards “topping up” telomeres without the risk of cancer. One form of such therapy that may be viable in the near future is through NMN supplements.
What is NMN?
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a naturally occurring molecule found in the human body and is known as an NAD+ precursor. The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an essential molecule capable of powering different cell functions, much like a battery providing energy to a small engine. By giving cellular energy, NAD+ can increase enzyme activity, gene expression, and cell signaling. However, as we age, our bodies face decreased NMN production, causing age-related diseases.
As mentioned earlier, telomeres tend to degrade with time and exposure to harmful environmental factors. Although our bodies do have molecular machinery to repair DNA, excessive DNA damage can drain cell resources. To counteract this loss, consuming an NMN supplement can provide an altered NAD metabolism and boost the DNA repair process, which in turn combats aging.
Learn more about the latest NMN research here: www.nmn.com
What are the health benefits of NMN?
A 12-month-long NMN research study on mice has shown that NMN is able to combat age-associated illnesses. Researchers from Washington University School have found that through oral administration of dietary supplements that older mice are capable of experiencing “anti-aging” effects such as:
- Suppressed weight gain and enhanced energy metabolism – age-associated weight gain results from fat retention, so growing energy production from NAD is found to increase exercise capacity and even fight metabolic disorders.
- Promoted physical activity levels – a study from the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition found that greater NMN supplementation had improved blood flow and skeletal muscle uptake of oxygen, leading to greater exercise endurance.
- Increased insulin sensitivity – helps cells increase blood glucose metabolism, lowering blood sugar levels and preventing progress into weight gain and type 2 diabetes.
- Improved eyesight – due to the replenishment of NAD levels, neurodegeneration is decreased, and vision is restored.
Given these NMN benefits in aged mice models, long-term administration may also provide positive anti-aging properties in humans.
Effects of NMN supplements on humans
NMN research shows great potential as an anti-aging supplement in several animal models, especially in aged mice. With the promising results, more human clinical trials have been conducted recently to compare the benefits and possible side effects of NMN. A study by the University of Tokyo on old, healthy Japanese men found that through consumption of dietary supplements over 12 weeks, NAD levels had doubled, and walking speed had increased. In addition, NMN supplementation has also improved muscle strength, which is an important clinical indicator of aging.
Before you start taking NMN supplements, it’s best to first seek professional medical advice. Depending on your age, you may need a specific dosage of NMN treatment to increase NAD levels, which can be up to 750mg per day. With more human trials underway, this versatile, anti-aging molecule may soon be used in mainstream supplemental health care.


